 Introduction Discovering the Problem Arsenic in Nature Source of Contamination Arsenicosis: Toxic Effects Feature of Arsenicosis Confirmation of Diagnosis Treatment Arsenic Detection De-arsination Control Measures WHO Recommendations Contact us © Copyright: MIG 1998 |
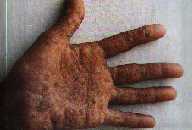
Arsenic
Contamination of Drinking Water Comparison of Arsenic Detection Methods
Field Kit Method The Department of Occupational and Environmental Health (DOEH), National Institute of Preventive and Social Medicine (NIPSOM), Dhaka has developed a low cost Field Test Kit for the detection of Arsenic in water and using it satisfactorily since 1995. WHO and World Bank have recognized the quality of the test kit. Mr. Hiromi Hironaka, a scientist working at the Asian Arsenic Network (AAN), has given the original formula of the kit. The DOEH modified the formula a little to make the procedure of use even simpler. The Local Field Kit is popularly known as NIPSOM Field Kit, which enables detection of arsenic up to 0.01 mg/L level. Figure-3: Testing of Drinking Water by Field Kit for Arsenic
Principle of the Field Kit method In ground water, arsenic remains in trivalent (arsenite) or pentavalent (arsenate) form. Arsenate is reduced to arsenite by potassium iodide and stannous chloride. Arsenite is then added to zinc and hydrochloric acid, which produce arsine gas. The arsine gas is treated with a specially prepared paper disk, which shows color change. The color developed in the paper disk is compared with a color scale to determine a range of arsenic level in the water sample. © Copyright: Medical Information Group
(MIG) 1998 |