
|
In legend, the God Dionysos was Nicaea's founder; according to record, some inhabitants of a small town of the same name near Thermopylai may have colonized it. Moreover, in that locality is noted an ancient military camp of Bottiei; and the city was named Elikore, Ankore, when in 316 B.C. Antigonos Monophthalmos founded Antigoneia there. Antigonos, who was a commander in Alexander the Greatís army and who had founded the city called "Antigoniea", died in 316 B.C. whereas the city passed over into the control of another commander called Lysimachos. Lysimachos developed and beautified the city which he renamed after his wife Nikaea. Following the death of Lysimachos in 293 B.C., the city was taken over by the Bthynians. It was only in 72 B.C. that Bithynia came under Roman domination at the conclusion of the Mithridatic war . Embellished under Augustus to the point of contending with Nicomedia for the seat of the provincial governor, Nicaea became the first city of the eparchy under Claudius, as we know from the coinage. Pliny the Younger, governor under Trajan, further enlarged the city. Hadrian visited Nicaea in 123 and undertook works of fortification that were finished in the 3d c. A.D. under Claudius II (Gothicus) , after the Goths had already caused serious damage to the city in 258. Constantine continued the work of embellishment of his predecessors, and held the first council at Nicaea in 325. Justinian took particular interest in the city, which was again chosen in 787 for the second council. In 1080, the Seljuk Sultan Kutalmisoglu Suleyman Shah captured the city and made it the Seljuk capital, but the Byzantines regained the city in 1097. In 1204, the Byzantines fled here during the Latin plunder of Constantinople whereas it remained their capital for 57 years. Orhan Gazi made the city a part of Ottoman territory in 1330 whereas the name was changed to its current name of IZNIK. Click the link to learn detailed HISTORY OF NICAEA.  The city lies in a fertile basin at the eastern end of the Ascanian lake (now called Iznik Golu. It is located near Orhangazi, 20 km / 12.5 miles from Yalova on the way to Bursa. The city lies in a fertile basin at the eastern end of the Ascanian lake (now called Iznik Golu. It is located near Orhangazi, 20 km / 12.5 miles from Yalova on the way to Bursa.Surface area:298 km≤ / 115 sq miles. The biggest lake in the Marmara region.Elliptical in shape. 12 km / 7.5 miles. Length :32 km / 20 miles. Depth:30 m / 100 ft. One of the deepest lakes. The deepest part is 65 m / 210 ft . Altitude:85 m / 280 ft Formation:Tectonic It is surrounded by olive trees, grapes and fruit gardens. The excess of water is carried to the Gemlik (Kios)Bay. More than 20 kinds of fish including mainly carp, pike and crawfish live in the lake), with its west wall rising straight of the water. Its wall was about 5 km long, about 10 m high with over a hundred towers. Outside the wall a double ditch gave further protection. Access through the wall was afforded by four main gates: the Istanbul Gate (in the north), the Lefke Gate (in the east), Yenisehir Gate (in the South) Gol (Lake) Gate. The west wall was also pierced with gates which gave access to wharfs and jetties, from which small boats plied across the lake. These boats gave the city a lifeline which made it impossible to blockade unless the attackers, too, had boats. It is bounded to the to the north and south by ranges of hills - especially apparent to the south where the ground rises sharply into the 800 m high Avdan Daglari range which overlooks the city. To the east, a wide and gently sloping valley leads away towards Ankara and the Anatolian Plateau. 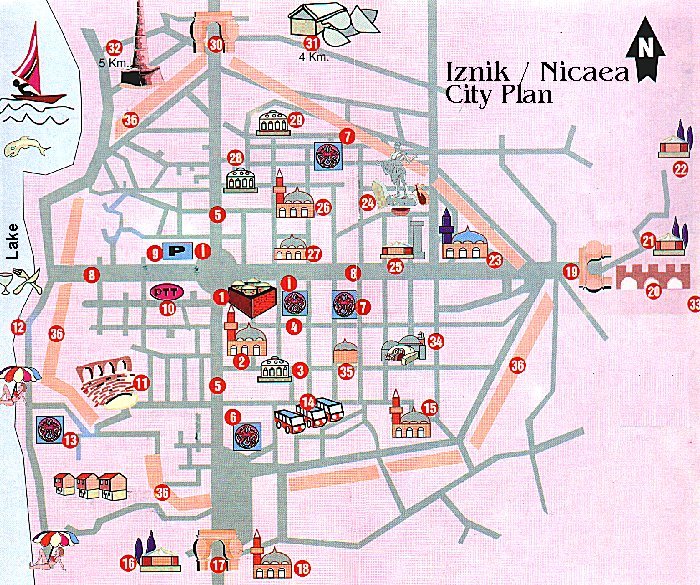  The geographical situation of Nicaea was particularly fortunate.  Its position on the shore of Lake Iznik (Ascania),on level and fertile ground, with wide roads for traffic that radiated from the city, made Nicaea a great Hellenistic center. Its position on the shore of Lake Iznik (Ascania),on level and fertile ground, with wide roads for traffic that radiated from the city, made Nicaea a great Hellenistic center.Strabo describes the foundation of the new Lysimachan city: "It had a square plan 700 m to a side; the roads were arranged with perpendicular axes, following the perfect regularity of the rectangular scheme; two large arteries crossed at right angles at the center of the inhabited area; the extensions of the roads led to the four gates of the city, visible from a fixed stone placed at the center of the gymnasium, a building that thus must be supposed at the heart of the urban plan". AQUEDUCT and the THEATRE of IZNIK 

 


 

 |