
 Cniderians &
Roundworms &
Mollusks &
Cniderians &
Roundworms &
Mollusks &
Segmented Worms &
Arachnids &
Crustaceans &
Mildew
Cniderians
1. All cnidarians have radial symmetry. Like sponges, a cniderian's body has only one body opening, and the body is made up of two cell layers. Cndarians have simple nervous system, and both cell layers have cells that can contract like muscles. the two cell layers are derived frm the ectoderm and endoderm of the embryo.
2. Surrounding the mouth of a cnidarian is a ring of flexible, tubelike extentions called tentacles. Tentacles can be long as in some jellyfishes, or short as in sea anemones and coals, but all are used for capturing.
3. Cell adapted for digestion inside the bodies of cnidarians release enzymes over the newly captured prey. The inner cell layer of cnidarians surrounds a space called a gastrovascular cavity in which digestion takes places. Any undigested materials are ejected back out through the mouth.
4. Cnidarian do not have a nervous system ad do complex animal; rather cnidarians possess a nerve net. A nerve net conducts parts of the body, but there is no control center like the brains of more complex animals. The impulses from the nerve net bring about contractions of musclelike cells in the tentacles and bodies of cndarian.
 Jellyfish
Jellyfish
Roundworms
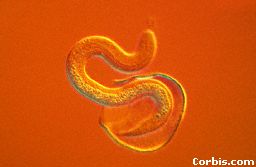
1. Roundworms are widely distributed, living in soil, animals, and both freshwater and saltwater environments.
2. Roundworms tend to be smaller than flatworms and are tapered at both ends. They have a thick outer covering that protects them from being difested by their host organisms. On a flat surface, roundworms look like tiny, wriling bits of sweing thread. Lacking circular muscles, they have pairs of lengthwise musles.
3. Roundworms have a pseudocoelom and are the simplest animals with a tubelike digestive system. It have two have two body opening- a mouth and an anus. The free species have well developed sense organs, such as eyespots, although these are reduced in parasistic forms.
4. Roundworms are found as parasites in most organisms on Earth. Nematodes can infect and kill pine trees, cereal crops, and food plants such as potatoes. Nematodes are particularly attracted to plant roots.
 Roundworms
Roundworms
Mollusks
1. Slugs, sanil, and animals that once lived in the shell on the beach are all mollusk. These organisms belong to the phylum Mollusca. Members of this phylum range from the slow moving slugs to the jet propelled octopus.
2. Mollusks live in a wide variety of habitats. Most live in marine or freshwater habitants, but some live on land. A few species of mollusks can be found in cold, polar regions, and many are common in warm, tropical areas.
3. Mollusks have soft bodies composed of foot, a mantle, a shell and visveral mass that contains internal organs. Comparison of these three body sections show how the bodies of the three classes of mollusks are adapted for survival.
4. Mollusk are the first animals to have evolved repiratory structures. These structures are called gills. Gill tissue increases the surface area through which gases can diffuse, and it contains a rich supply of bood for the transport of gases. while aquatic gastropods have gills, the matle cavity of land snail and slugs has evolved into a primitive lung.
 Mollusks
Mollusks
Segmented Worms
1. Segmented worms live everywhere except in the frozen soil fo the polar regions and the dry dsand and soil of deserts.
2. Earth worm burrows through soil, it loosens , aerates, and fertilizes the soil. Burrows provide passageways for plant roots and improve drainage.
3. Earthworms are nocturnal animals that live in burrows. A nocturnal animal is one that moves about primarily at night. At night, earthworms come to the surface but stay close to their burrows.
4. The cool, moist soil provides protectio for the worms during day. Water in the soil is a source of oxygen that diffuses into earthworm's body through the skin.
 Segment Worm
Segment Worm
Arachnids
1. Arachnids are spiders, scorpions, mites, and ticks belong to the class arachnida. Spider are the lasrgest group of arachnids. Whereas most arthropods have three body regions, the arachnids have no distinct thorax and therefore have onl two body regions.
2. A narrow waist (pedicel) connects both parts. The upper side of the spider is called the dorsal side (i.e. the back) and the bottom the ventral side (i.e. the belly). The cephalothorax at the dorsal side is made of chitin what is called the carapax. The eyes are located in the front. Most spiders have eight eyes, some 6. But there are spiders with no eyes, 2, 4 and up to even 12 eyes. The eyes are singular and are called ocelli, unlike the insects that have compound eyes.
3. The back the prosoma is called the abdomen or opisthosoma. Directly behind the head is a groove, the fovea. The zone just behind the eyes is called the clypeus (forehead). The part on the dorsal site between the legs is called sternum. The palps in the front are used for sensory purposes. In the male the palps are modified for putting sperm into the epigyne of the female, that is situated on the underside of the abdomen.
4. The jaws are located below the eyes and are called chelicera. The piercing parts of these jaws are the fangs that deliver the poison via a small hole at its tip.
 Arachnids
Arachnids
Crustaceans
1. All crustacean have mandibles for crushing food, two pairs of antennae for sensing, and two compound eyes, which are ussually located on movable stalks.
2. Unlike the up and down movement of our jaws, crustacean mandibles open and closes from side to side. Five pairs of walking legs are used for walking, for seizing prey, and for cleaning other appendages.
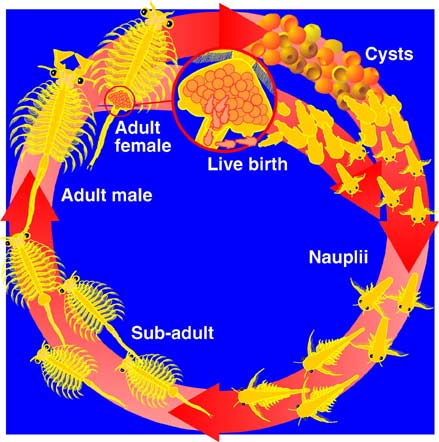
3. For example The brine shrimp, Artemia,belongs to the phylum Arthropoda (joint-legged invertebrates), class Crustacea (shrimp, crab, lobster). There are several species of Artemia worldwide; Artemia franciscana is the species living in Great Salt Lake (and also in San Francisco Bay). Brine shrimp live in hypersaline lakes in which the salt content may be 25%, predators and competitors are few, and algal production is high. The life cycle of Artemia begins from a dormant cyst that contains an embryo in a suspended state of metabolism (known as diapause). The cysts are very hardy and may remain viable for many years if kept dry.
4. Like the Mitten crabs spend most of their life in fresh water, but they have to return to the sea to breed. During their fourth of fifth year, males and females migrate downstream attaining sexual maturity in the tidal estuaries. This migration occurs during late summer. After mating the females continue seaward, over-wintering in the deeper water and returning to brackish water in the spring to hatch their eggs.
 Grapsuscrustacean
Grapsuscrustacean
 lifecycle of a crab
lifecycle of a crab
Mildew
1. a conspicuous mass of threadlike hyphae and fruiting structures produced by various fungi (division Mycota).
2. It is associated with cloth, fibres, leather goods, and plant diseases (downy mildew and powdery mildew [qq.v.]).
3. The fungi use these substances as sources of food for growth and reproduction.
4. Downry mildew is a disease of plants, especially in cool humid regions, caused by several fungi, including species of Basidiophora, Bremia, Peronospora, Phytophthora, Plasmopara, Pseudoperonospora, and Sclerospora. White, gray, bluish, or violet downy patches of mildew form mostly on the undersides of leaves in damp weather.
 Mildew
Mildew
 InDeX
InDeX
TOP










 InDeX
InDeX