Einstein's special relativity, created a system bounded by the expansion of energy at the speed of light(c).
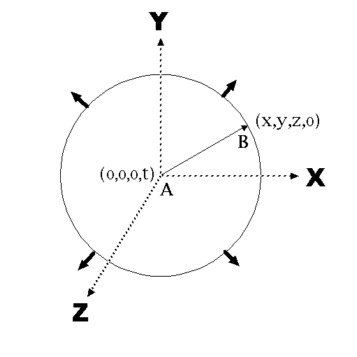 The above figure shows an expanding wave which has generated a closed spacetime sphere with a radius
dimensionally equal to the line A,B. The wave occurs when a light producing event at location (0,0,0,0)
generates the closed spacetime field which is being observed after
time t seconds has passed. The length of line A,B becomes ct which
is a distance in spacetime. The center of the sphere is at the new spacetime point of (0,0,0,t)
in which the spatial dimensions have not changed but the clock time has the new value t. The outer surface of the closed system has become the surface of the sphere with the radius ct, the point B then has
the spacetime location ( x,y,z,0) because the spatial dimensions have changed
but the time dimension still has the initial event value of 0.
The above figure shows an expanding wave which has generated a closed spacetime sphere with a radius
dimensionally equal to the line A,B. The wave occurs when a light producing event at location (0,0,0,0)
generates the closed spacetime field which is being observed after
time t seconds has passed. The length of line A,B becomes ct which
is a distance in spacetime. The center of the sphere is at the new spacetime point of (0,0,0,t)
in which the spatial dimensions have not changed but the clock time has the new value t. The outer surface of the closed system has become the surface of the sphere with the radius ct, the point B then has
the spacetime location ( x,y,z,0) because the spatial dimensions have changed
but the time dimension still has the initial event value of 0.
 DYNAMIC IMAGE OF CLOSED SYSTEM SHOWING CLOCKS IN A FIXED SPACE FRAME
DYNAMIC IMAGE OF CLOSED SYSTEM SHOWING CLOCKS IN A FIXED SPACE FRAME
Effectively the spacetime field has radiated from the electromagnetic
event which gave rise to the light wave. The interesting result is that
the spacetime sphere has the maximum PAST time at the center and the present
at the surface (using the scalar clock time paradigm)
One feature noted from the closed sphere is that the outer surface represents the present and the inner volume represents the past as a real
spacetime dimension. The spacetime oustide the sphere represents the
future or imaginary spacetime field which cannot contain any energy
related to the event and cannot be predicted as a medium for the
spacetime continuum being considered. The above closed system is represented by the equation
shown below.
x 2 + y2 + z2 -
c2 t 2 = s 2As s = 0 (for a photon) this equation becomes a sphere.

 DYNAMIC IMAGE OF CLOSED SYSTEM SHOWING CLOCKS IN A FIXED SPACE FRAME
DYNAMIC IMAGE OF CLOSED SYSTEM SHOWING CLOCKS IN A FIXED SPACE FRAME