Using the Minkowski flat space metric (timelike configuration) (c/f the spacelike example in the ref section)
and the equation for the spacetime point
![]()
for a light cone type of visualization in which (S = 0)
the equation becomes
![]()
which becomes the sphere with radius cdt
![]()
using the Minkowski metric for positive flat space
the dx, dy, dz coordinates are based on a center
(0,0,0) time t after an electromagnetic event at (0,0,0)
the SPACETIME coordinate becomes (0,0,0,t)
In order to generate an easy to visualize image
I suggest a (LIGHT) sphere surface radiating from the
Event location at the velocity c (speed of light in a vacuum).
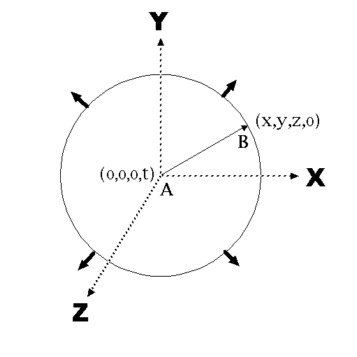
Note that AB must be reversed to conform with the original metric
This demonstrates that the time function is zero at the surface of the sphere and has a positive value at the electromagnetic event location
This figure shows that the spacetime inside the sphere represents the PAST, the surface represents the PRESENT, and the FUTURE is the space outside the light sphere.
The surface of the light sphere represents the cone surface for the light cone.
DIFFERENCES between the time cone and the time sphere
1/ The light cone relates to the Minkowski time line whereas the time sphere relates to a single event point in spacetime
2/ All information relating to energy change after the event is contained within the light sphere
3/ Time being a scalar the locus of the sphere surface represents a vector field of time lines (direction undefined) radiating from the center.
4/ The sphere does not include the undefined spacetime 5/ The sphere adds an additional spatial element which enables visualization approximating the real world as usually visualized by the mind. SIMILARITIES 1/ Both images include space and time as a visualizable image Note The spherical surface can also be viewed as the event horizon of a black hole (non flat spacetime s=0,c=0) For a (flat Minkowski spacetime), as envisaged by general relativity. The flat version is the basic photon condition in which c=1 relative to the event in timelike frame c= 300,000,000 meters/sec