Photosynthesis: Questions
Here are some questions regarding the photosynthesis part of my site.
Multiple choice questions
A. P670
B. P680
C. P700
D. P600
A. P670
B. P680
C. P700
D. P600
A. photosynthetic efficiency
B. rate of photosynthesis
C. irradence level
D. light saturation point
A. C3 plants
B. C4 plants
C. CAM plants
D. All of the above
A. 19%
B. 24%
C. 5%
D. 8%
A. True
B. False
A. ATP-ase
B. Z protein
A. proton gradient
D. B6-f complex
A. Only found in photosystem I
B. Only found in photosystem II
C. Responsible for cyclic electron flow
D. An accesory pigment
A. NADPH
B. NAD+
C. Protons
D. ATP
A. G3P is the primary end product of the Calvin cycle.
B. G3P may be transported into the vascular bundles and and used to produce glucose or sucrose.
C. G3P may be converted into glucose and polymerized into startch within the stroma of chloroplasts.
A. They are all true
A. Irradance
B. Light-compensation point
C. Photosynthetic
D. Rate of photosynthesis
A. photosystems
B. chlorophyll a
C. Z protein
D. enzymes
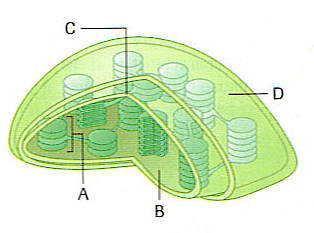
|
A. A-Thylakoid disk
. B-Thylakoid lumen . C-Inner membrane . D-Chloroplast |
B. A-Stacks of photosynthetic reaction sites. . B-Thylakoid lumen . C-Inner membrane . D-Outer membrane |
C. A-Lamella . B-Thylakoid . C-Inner membrane . D-Thylakoid disk |
D. A-Granum . B-Stroma . C-Inner membrane . D-Outer membrane |
A. Carotein
B. Chlorophyll b
C. Chlorophyll a
D. both B and C
A. K+ ions
B. H+ ions
C. Osmosis
D. all of the above
A. True
B. False
A. 4
B. 3
C. 12
D. 7
A. Thylakoid space
B. Stroma
C. Cytoplasm
D. Stoma
A. photosystems
B. enzymes
C. accessory pigments
D. proteins
A. There is none, the difference is in the proteins they associate with in the photosystem.
B. chlorophyll a contains a methyl group where chlorophyll b contains a aldehyde group.
C. chlorophyll b contains a methyl group where chlorophyll a contains a aldehyde group.
D. The phytol chain is longer in chlorophylla than it is in chlorophyllb
Cuticle:
Epidermis Layer:
Mesophyll Layers:
Guard Cells:
Stomata (stoma):
Transpiration:
Vascular bundles:
Stroma:
Thylakoids:
Grana (granum):
Lamellae (lamella):
Thylakoid membrane:
Thylakoid lumen:
1. How does transpiration assist the photosynthetic process?
2. Why do plants appear green?
3. What is an accessory pigment?
4. Describe and explain Priestley's experiment.
5. Why do plants change from green to red-orange-yellow in the fall?
1. What begins the process of photosynthesis (light reactions)?
2. Summarize the steps in noncyclic electron flow.
3. Describe the 3 phases of the Calvin Cycle.
4. Describe the difference between C3 plants and C4 plants.
2. How do guard cells control the size of stomata?
3. What dimensions does a typical plant cell chloroplast have?
4. Describe the internal structure of a chloroplast.
5. What is the endosymbiotic theory?
6. What is the overall equation for photosynthesis?
7. What is Cyclic Electron Flow?
8. What is the Calvin Cycle?
9. Name the main differences between photosynthesis and cellular restpiration
10. What is a photon and a photosystem?
11. What are alternative mechanisms of carbon fixation?
| Back to Biology | Back to Sciences |