

The Romans put a great
deal of effort into engineering. Roman engineering led to the building of
some remarkable engineering feats that have survived to this day
throughout western Europe - be they roads, theatres, baths or Hadrian's
Wall. Engineering was used as a way of improving the lifestyle of the
Romans even on day-to-day issues such as a frequent water
supply.



Aqueducts were made from a line of arches joined together, with a channel on the top to carry water. The Romans used them to supply towns with water. The arches would be higher or lower as the aqueduct covered rough ground but it would always have a slight slope towards the town so that the water could run downhill.
The Romans used the ideas of the Ancient Greeks to implement their own engineering plans. The whole issue of supplying Rome with water was solved using a system of 640 kilometers of aqueducts. The aqueduct at Segovia in Spain is 60 meters high in places. The fact that it has survived so long and in its current condition is testament to the engineering skills of the Romans.

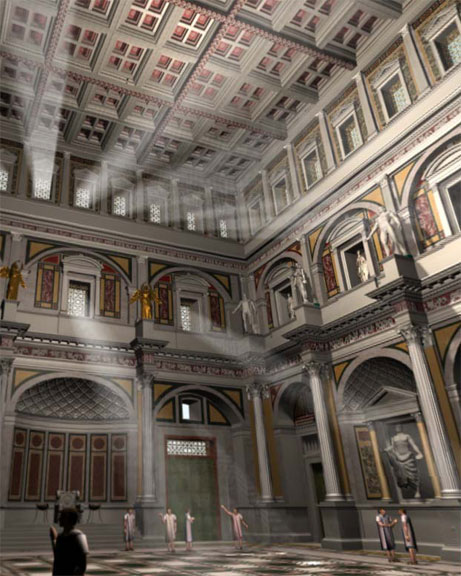
The Roman Baths

One of the
characteristic Imperial Roman building types is the giant bath complex
which could house not only bathing facilities but lecture halls, gymnasia,
libraries and gardens.
Roman baths
were more like a visit to a leisure centre than a quick scrub. The Romans
loved the baths because they were a good place to meet people and business
could be conducted there.
When you went to the baths you firstly
changed out of your clothes and did some exercises. Then you might have a
swim in the pool before going into a series of rooms which got hotter and
hotter to help make you sweat off the dirt.
When the Romans
were in these rooms they would often stop and talk to each other. All the
dirt and sweat was then scraped off with a strigil and you had a
swim in the cold pool.
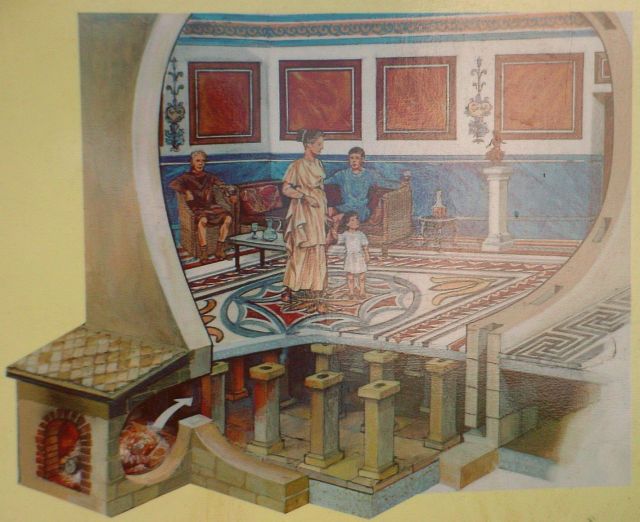
The Roman System of Heating
The Romans were good at building and engineering, but not so good at inventing machines. There were always plenty of slaves to do the nasty jobs, so nobody bothered to think up machines that could take their place. An example of this was central heating which involved lots of effort from Roman slaves. Public baths and rich people's houses all had central heating.
Houses were also centrally heated by what was known as a hypocaust. This was under-floor heating. Slaves were charged with keeping the hypocaust both clean and alight during the day. This system of heating was also used to keep some Roman baths hot.
Roman Sanitation
The Romans also invented the best drains in the world. Towns and forts had underground drains to take away dirty water and sewage. They were flushed through with water from the baths so that they didn't get too smelly.
Fresh clean water and sewers are important
because without them people often catch diseases from drinking dirty water
or from sewage left around the streets and houses.
Instead of toilet paper, Romans used a sponge tied to
the end of a stick!
Public Toilets, Ostia, first century BC
 ACTIVITIES
ACTIVITIES
1. Put on a new page in your book the
heading: Roman Technology and Building.
Answer the following
questions in complete sentences in your book.

Fig.A

b) Study the reconstructions of the city of Ancient Rome.
3. Why was it so important for the Romans to have an effective sanitation system in their city?
4. Explain in your own words how the Romans heated their houses and pools.
5.Draw,colour and label fig.A in your book.
6. How did the Romans get fresh water into their cities and houses?
7. Why were public baths important in Roman society?

8. What is this tool and how was it used?
 |
The Pantheon at Rome was built by Agrippa in 27 BC, destroyed, and rebuilt in the 2d cent. by Hadrian. Remarkably well preserved, it is mainly of brick with a great hemispherical dome whose supporting walls are set in concrete. |


An artists impression of a wealthy Romans county villa.
Houses also had water piped straight to them - unlike flats and apartments. Lead pipes brought water to a house. However, these pipes were taxed according to size - the larger the pipes, the more the tax. Archaeologists can usually tell the wealth of an owner of a Roman house by simply looking at the size of the lead pipes that brought water to that house.

Roman Roads

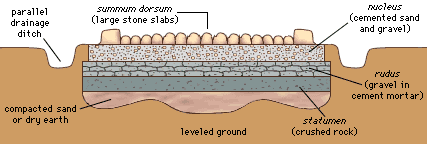
Roman roads were famed for being straight and well made.
Surveyors used a tool called a groma.
This was an instrument that had two
pieces of wood nailed together so that they formed a square cross with
right-angles in all the corners. Each piece of wood had lead weights
attached to the ends. When one lead weight from the same piece of wood
lined up with the one in front of it, the surveyor knew that he had a
straight line.
9. Write out and complete the following
sentences in your book:
a) The two main reasons that the Romans needed
good roads are...
b) The groma was an important Roman surveying tool
because...
10.
Draw, label and colour the above cross-section diagram of a Roman
road.
The Roman Road System at the height of the Empire.

The Romans were famous for their roads. Some Roman roads exist to this day, nearly 2000 years after they were made. Roman roads were superbly made. Why did the Romans put so much effort into building roads?
Rome made a great deal of money from trade in Europe. Some of this trade involved transport by sea. More frequently, the Romans used roads. Also with so much of Western Europe conquered by the Romans, the Romans needed roads to move their troops around quickly. Poorly built roads would not help this.



http://www.earlybritishkingdoms.com/kids/romans/roman_houses.html
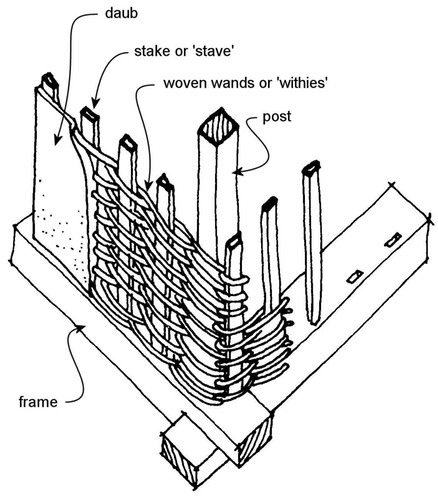
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wattle_and_daub
a) Describe one of the methods the Romans used to build the walls of their houses.
b) Explain what the Romans put on the roof of their houses.
14. Go to the following site and complete the animated activity on building a Roman Aqueduct. Then in your book, under the heading More on Roman aqueducts, list three interesting facts that you discovered from doing the animated building game.
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/lostempires/roman/aqueduct.html
www.interactive-learning.com.au