
 Basidiomycotes &
Other Invertebrate Chordates ( sea squirt) &
Sporozoa &
Basidiomycotes &
Other Invertebrate Chordates ( sea squirt) &
Sporozoa &
Ciliophora &
Birds &
Mammal
Basidiomycotes
1.Basidiomycota are club fungi. This division reproduces sexually; they get their name from their reproductive structures called basidiocarps. Mushrooms, shelf fungi, puffballs, and stinkhorns are all basidiomycotes.
2.Most basidiomycotes produce haploid basidiosprores on club shaped basidia. Typically, four basidiospores develop at the end of each basidium.
3. Phylum Basidiomycota — basidium ("club fungi") is a swollen tip on the hyphae where nuclear fusion, meiosis occur; complete hyphal cross walls (puffballs, edible mushrooms, bracket fungi). Basidiomycotes commonly form ectomycorrhizae (fungal hyphae envelope the root but do not penetrate the tissues) with forest trees, shrubs.

Basidiomycotes
Other Invertebrate Chordates ( sea squirt)
1. The chordastes most familiar to humans are the vertebrate chordates. However, a few invertebrate chordates have no backbones.
2. The terms chordata refers to the long semirigid, rodlike structure called notochord, which is common to all members of the phylum chordata. During the embryologic development of vertebrate chordates, this structure becomes the backbones.
3. The physical support of a notochord enables invertebrate chordates to make powerful side to side movements of the body. These movements propel he animal through the water at a much faster speed than would be possible if the body have no support.
4. The dorsal nerve cord is a bundle of nerves housed in a fluid- filled canal tha lies above the notochord. In most adult chordates, the posterior portion of the dorsal nerve cord develops into the spinal.

sea squirt
Sporozoa
1. Protists that are grouped in the phylum Sporozoa are called sporozoans. They are al parasitic, nonmotile protozoan.
2. Sporozoans get their name from the fact that many of them produce spores. A spre is a reproductive cell that can produce a new organism without fertilization.
3. Living as internal parasites in one or more hosts, sporozoans have complex life cycle.
4. Probably the best know sporozoans are members of the genus Plasmodium. Different species of plasmodium cause he disease malaria in people, some other mammals, and birds.
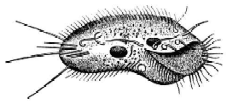
Sporozoa
Ciliophora
1. The roughly 8000 members of phylum Ciliophora, known as ciliates, move by the synchronized beating of cilia
that cover their bodies.
2. Ciliates are found in every kind of aquatic habitat, from ponds and streams to oceans and sulfur springs.
3. Paramecia usually reproduce asexually, with the cell dividing crosswise and separating into two daughter cells.
But when food supplies dwindle or environmental conditions degenerate, paramecia can also undergo a form of
conujation.
4. In this complex process, two paramecia come together and exchange genetic material through their oral groves.
After becoming genetically altered in this way, the two individuals separate, and each goes on to divide asexually.
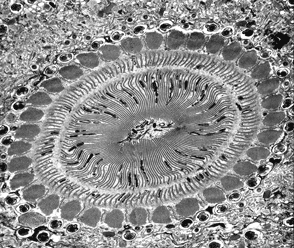
Ciliophora
Birds
1. Birds can be defined simply as the only organism with feathers. A feather is a lightweight, modified scale that provides insulation and enables flight. You may have seen a bird running its bill through its feathers while sitting on a tree branch or on the shore.
2. This process, called preening, keeps the feathers in good flying condition. The bird also uses its beak to rub oil from a gland near the tail onto the feathers.
3. A second adaptation for flight in birds is the modification of the front limbs into wings. Powerful flight muscles are attached to a large breastbone called the sternum and to the upper bone of each wing.
4. The sternum looks like the keel of a sailing boat and is important because it supports the enormous thrust and power produced by the muscles as they move to generate the lift needed for flight.

Bird
Mammal
1. Mammals also have organs called glands that secrete various substances needed by the animal. A gland is a cell of group of cells that secretes fluids. Mammals have several kinds of glands, including glands that produce saliva, milk, digestive enzymes, and hormones.
2. A supply of food must be available to produce the level of energy required to maintain a steady body temperature. Mammals have several adaptations that help them meet their nutritional needs.
3. Teeth are distinguishing feature of most mammals. By examing the teeth of a mammal, a scientist can determine what kind of food it eats. Although fishes and reptile have teeth, their teeth are relatively uniform and are used primarily for tearing, grasping, and holding prey.
4. Mammals have different kinds of teeth adapted to the type of food they eat. Many hoofed mammals have an adaptation called cud chewing that enables them to break down the cellulose of plant cell walls into nutrients that they can use and absorb.

Dolphin
 InDeX
InDeX
TOP








 InDeX
InDeX